- Obniżka

 Dostawa
Dostawa
Wybierz Paczkomat Inpost, Orlen Paczkę, DHL, DPD, Pocztę, email (dla ebooków). Kliknij po więcej
 Płatność
Płatność
Zapłać szybkim przelewem, kartą płatniczą lub za pobraniem. Kliknij po więcej szczegółów
 Zwroty
Zwroty
Jeżeli jesteś konsumentem możesz zwrócić towar w ciągu 14 dni*. Kliknij po więcej szczegółów
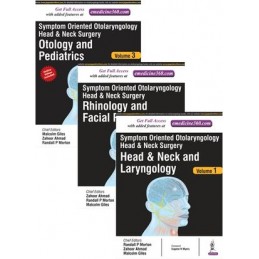
Symptom Oriented Otolaryngology:: Head & Neck Surgery - Three Volume Set is an extensive, illustrated review of a broad range of symptoms in otolaryngology, edited by a team of New Zealand based experts in the field.
The three volumes are each divided into two sections. Each section begins with the anatomy of the structures concerned, followed by chapters on associated symptoms and their diagnoses. The first volume covers head and neck, and laryngology, and the second volume covers rhinology and facial plastics. The final volume covers otology, with a section on paediatrics which includes nasal, oral, oesophageal and otological symptoms, including guidance on choking and swallowing difficulties.
This comprehensive book is enhanced by 900 full colour images across 1200 pages, making this an essential resource for consultant otolaryngologists and residents.
Key Points
Opis
Volume 1
Section One:: Head and Neck
Section Two:: Laryngology
Volume 2
Section One:: Rhinology
Section Two:: Facial Plastics
Volume 3
Section One:: Otology
Section Two:: Paediatrics
Indeks: 76298
Autor: Samuel David
Indeks: 99239
Autor:
